Previous
Next
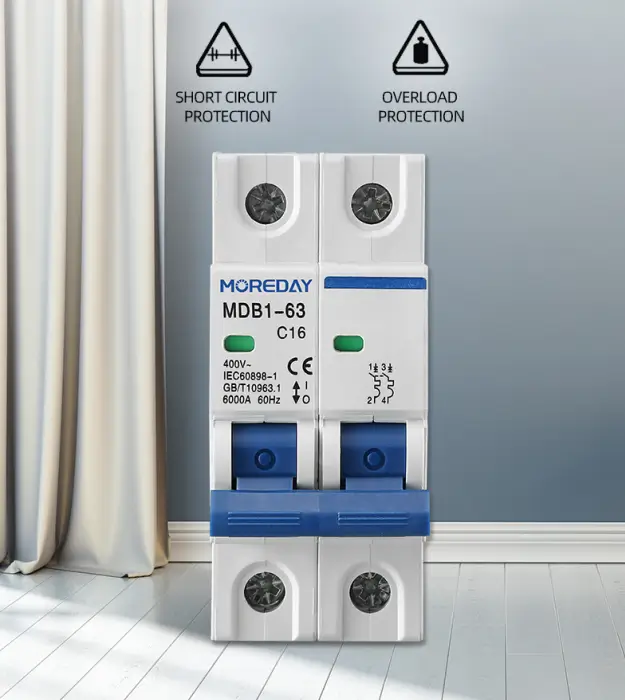
AC MINIATURE CIRCUIT BREAKER MDB1-63 6KA 63A IEC
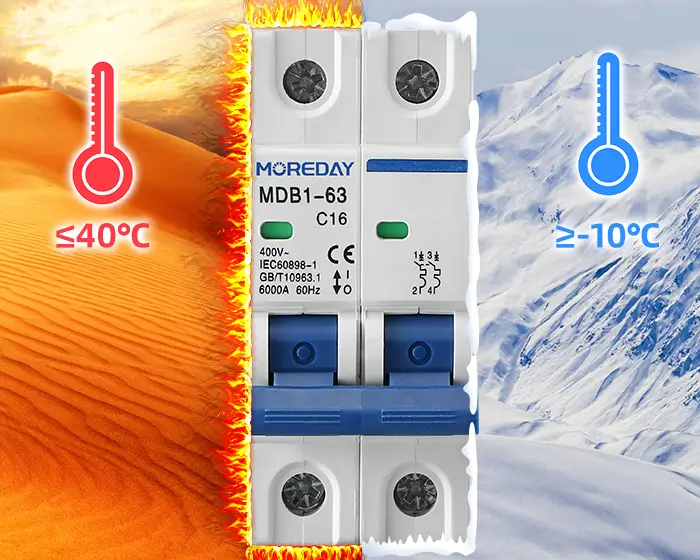
Suitable for industrial, commercial, high-rise, and civil residence circuit protection.
Features:
- Up to 63A current rating
- Current limiting design
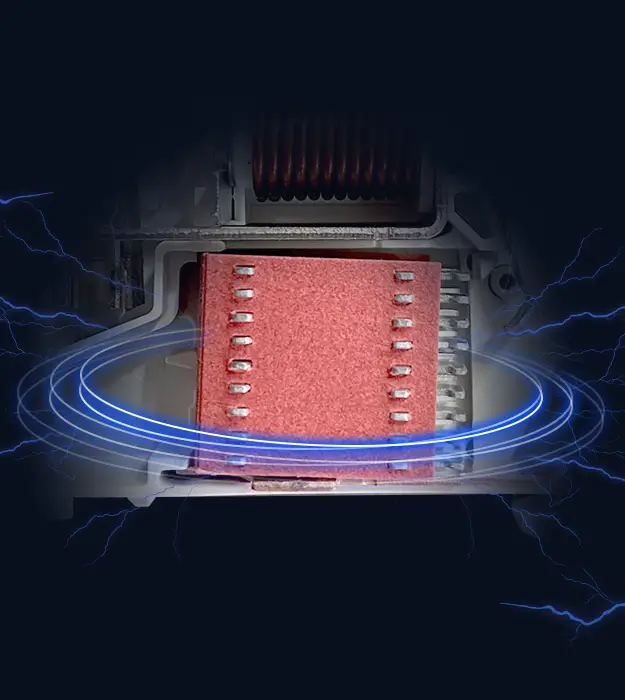
- Three levels of short-circuit protection,B、C、D curves.
- Housing: pluggable design
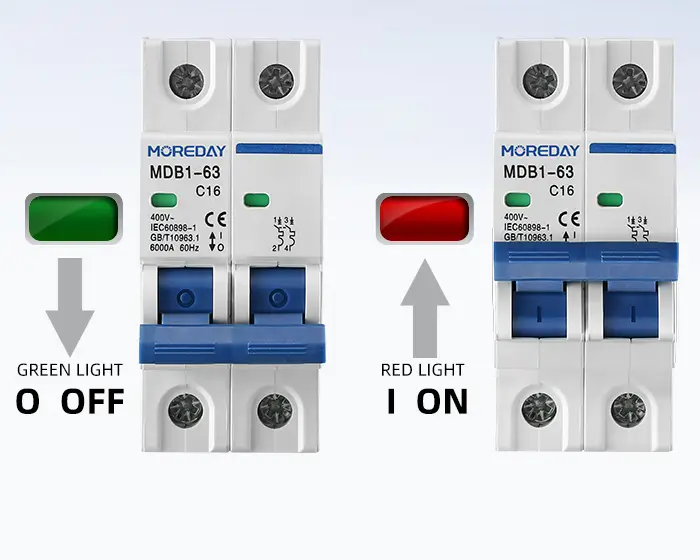
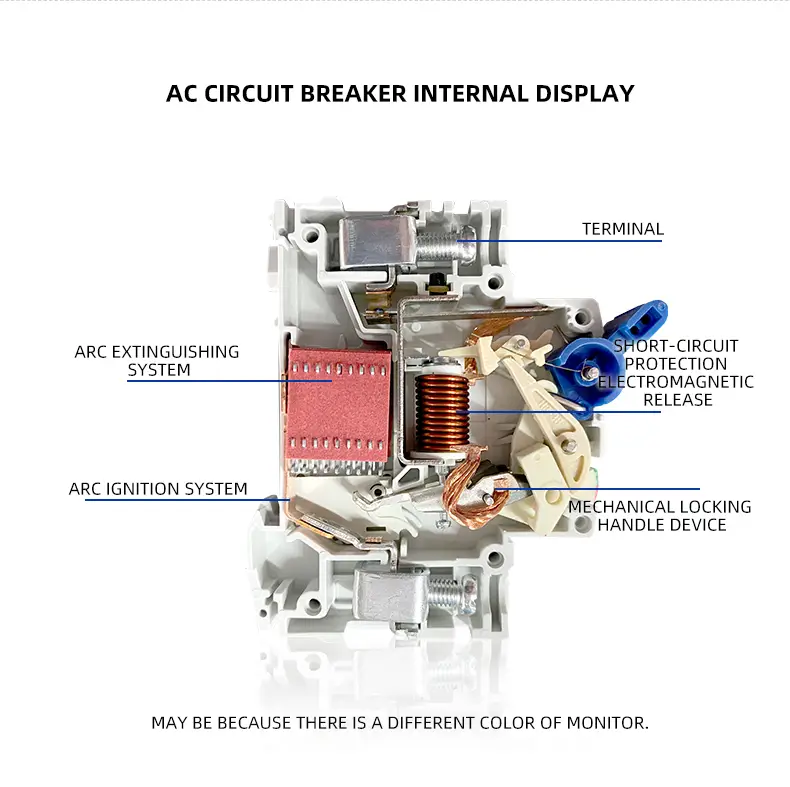
- Contact position indicator(red/green)
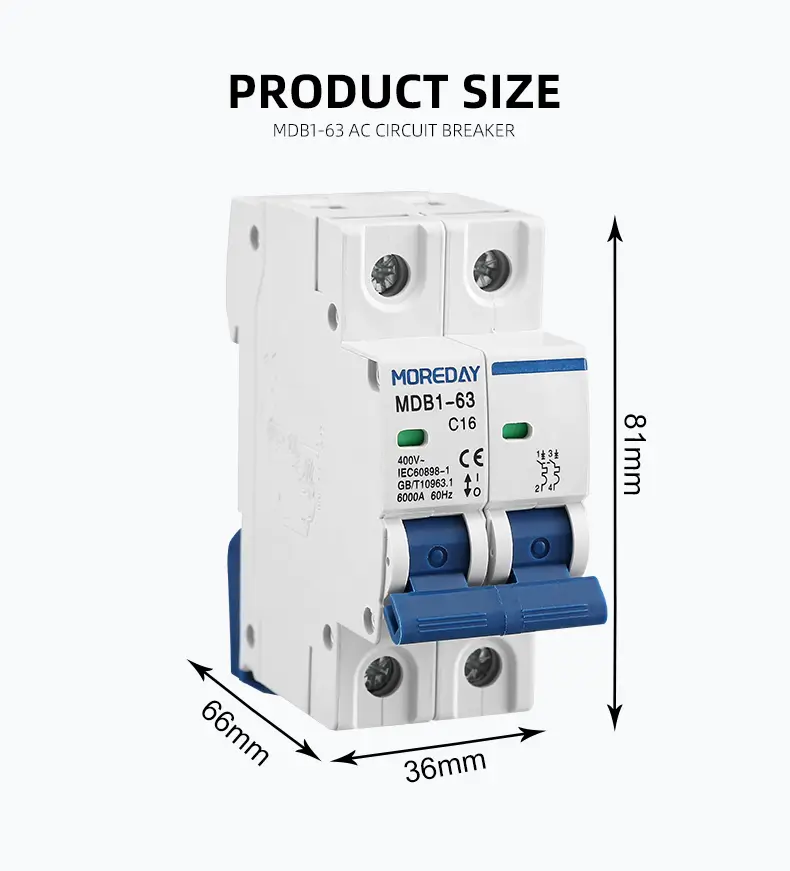
- Easy installation on din rail